Product Overview
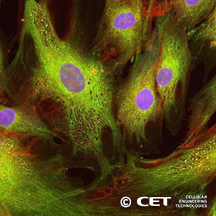
Cells derived from adult human lipoaspirate tissue collected during elective surgical liposuction procedures and then programmed using our patented virus-free method using episomal DNA and our proprietary mix of vectors, excluding Myc and Lin28 transcription factors. Adipose-derived mesenchymal cells (AdMSCs) are the most commonly used mesenchymal stem cells for clinical applications.
The cell line was validated for pluripotency based on colony morphology, alkaline phosphatase expression and expression of SSEA-4. Cells are free of Mycloplasma and exhibit classical morphology and growth characteristics. Vial contains approximately 500,000 cells. Shipped with dry ice.
AdMSCs have shown significant promise in treating autoimmune and neurodegenerative diseases, vascular and metabolic diseases, bone and cartilage regeneration and wound defects. These cells have been reported to differentiate into many different lineages including chondrogenic, osteogenic, adipogenic and neural cells.